Bioswales and (Bulb) Planting
More efficient use of rainwater in wet gardens and moist public spaces
A Sustainable Synergy
Bioswales play a crucial role in climate-adaptive landscape design. By incorporating flower bulbs around bioswales, you not only improve water drainage efficiency but also enhance biodiversity and visual appeal. This combination fosters a healthier ecosystem while creating a more attractive environment for residents and visitors alike.
On this page, you'll discover how flower bulbs seamlessly integrate into bioswale designs, which species thrive best, and how to apply them effectively for a sustainable and flourishing landscape.
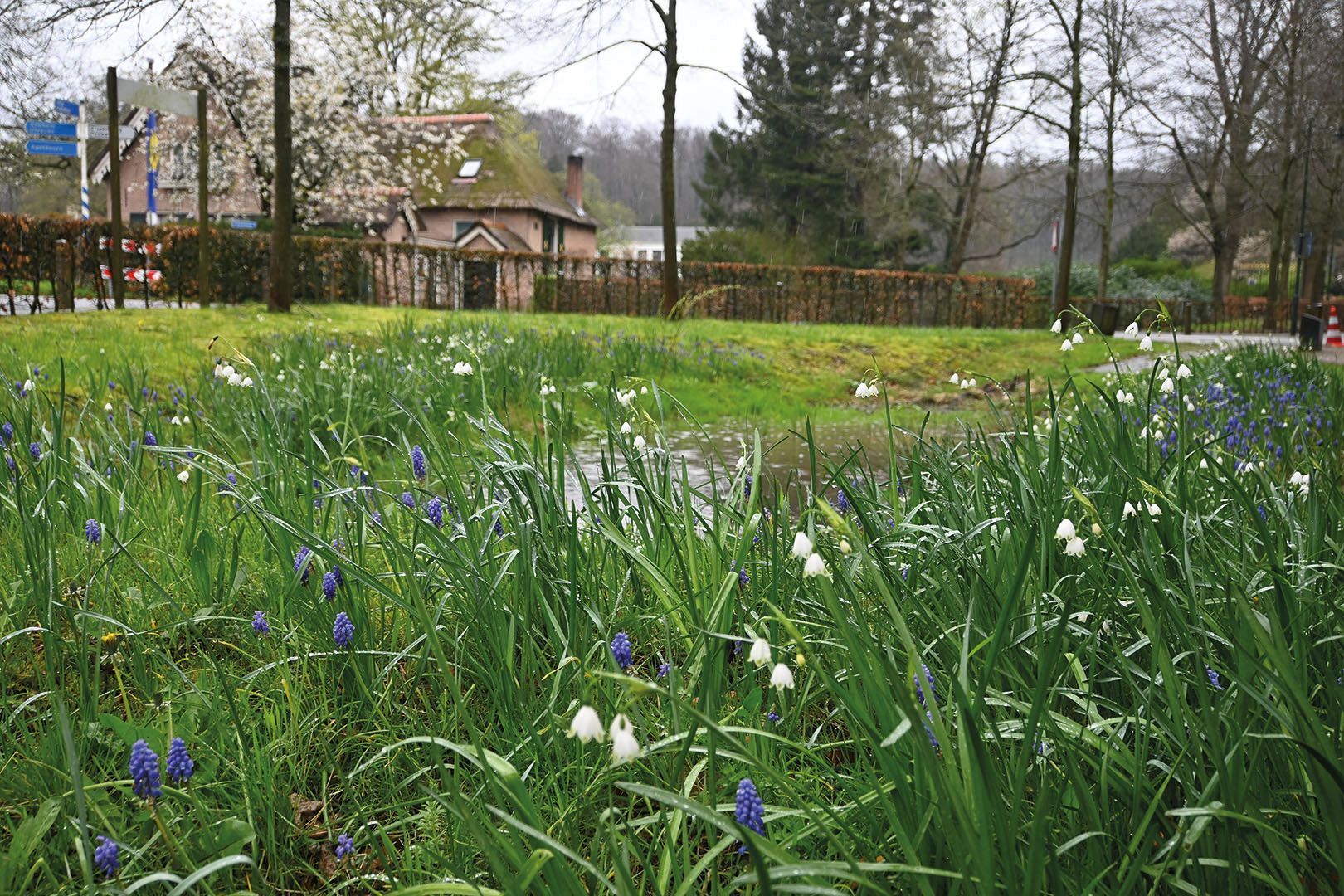
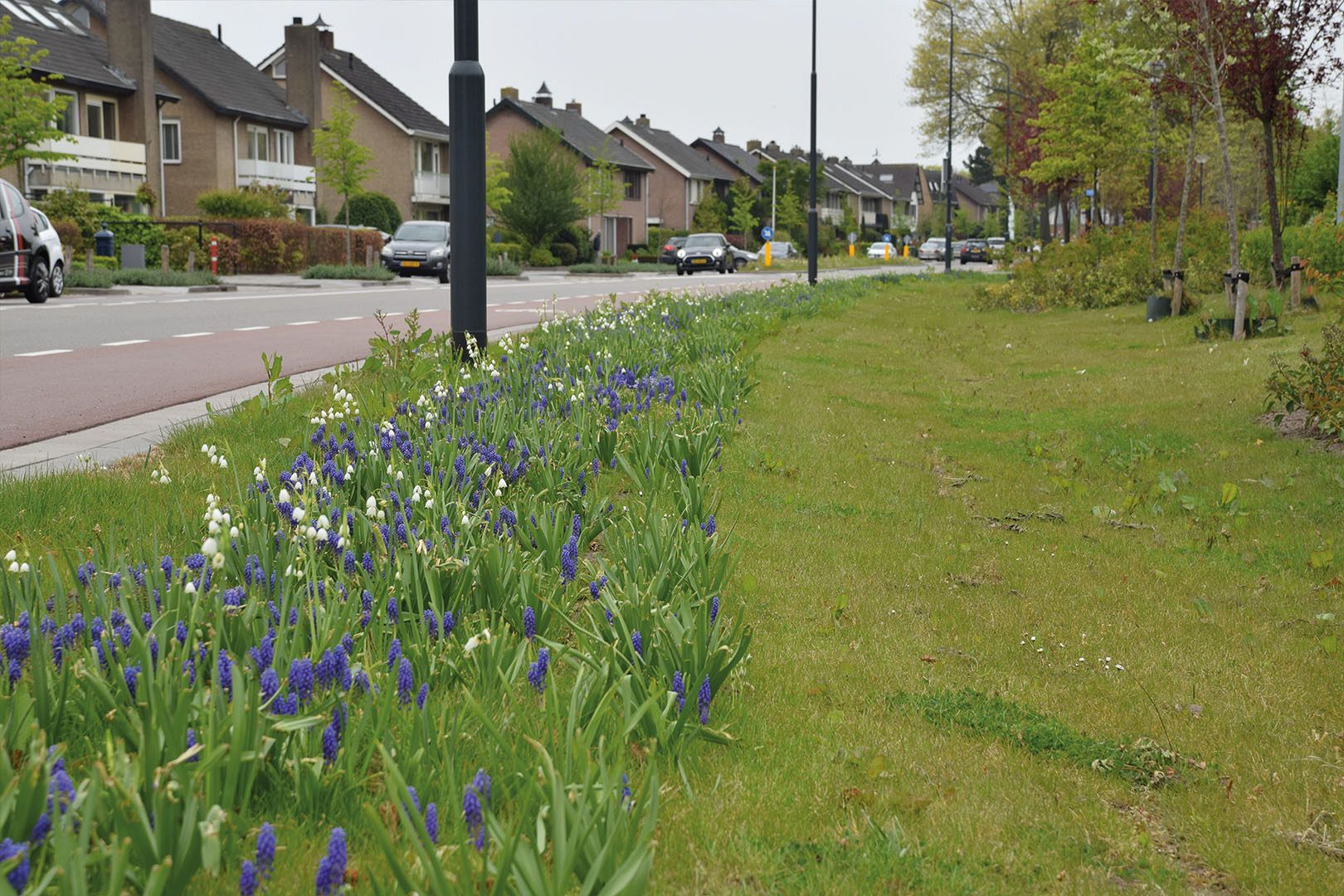


What is a Bioswale?
An innovative and specially designed type of wetland area is the so-called bioswale. A bioswale functions similarly to a floodplain or riverbed, designed to temporarily collect and filter rainwater. It allows water to slowly infiltrate into the ground, reducing the strain on drainage systems and preventing urban flooding.
A well-designed bioswale system helps regulate water overflow, improves surface water quality, and mitigates drought conditions. It typically consists of a vegetated upper layer with a permeable soil base that enhances water absorption and filtration.
Bioswale systems are engineered to handle a specific volume of water. They are usually designed for a maximum water depth of several inches, temporarily holding water for a short period—typically no longer than a day—before it gradually drains away. Most of the time, bioswales remain dry.
A rain garden is a similar concept but on a smaller scale. It is a shallow, planted basin designed to capture and temporarily store rainwater after heavy rainfall. The vegetation helps retain water, allowing it to slowly infiltrate the soil while also promoting evaporation. Like bioswales, rain gardens remain dry most of the time.
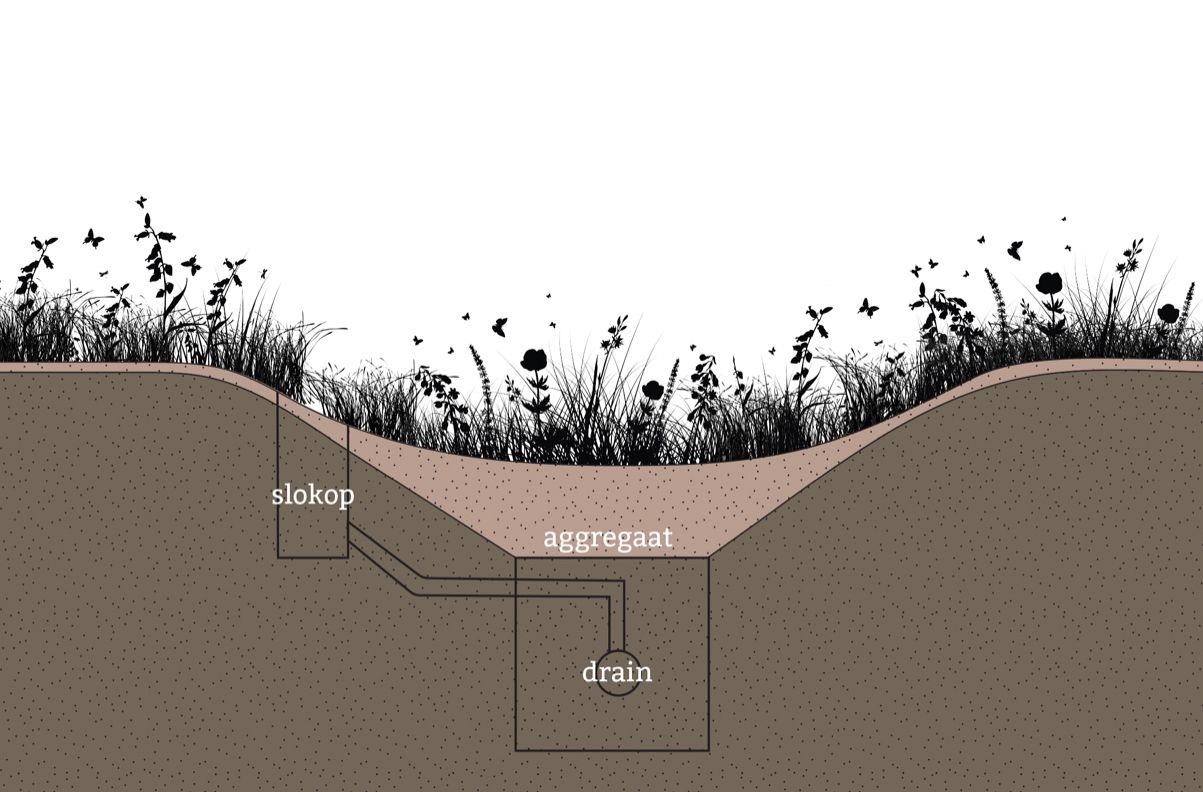
Dry Bioswale
The illustration shows a bioswale in its dry state. Through infiltration, rainwater is gradually absorbed into the groundwater, contributing to better water management. During wet periods, a bioswale typically does not remain dry for long, as it serves as a catchment area for excess water.
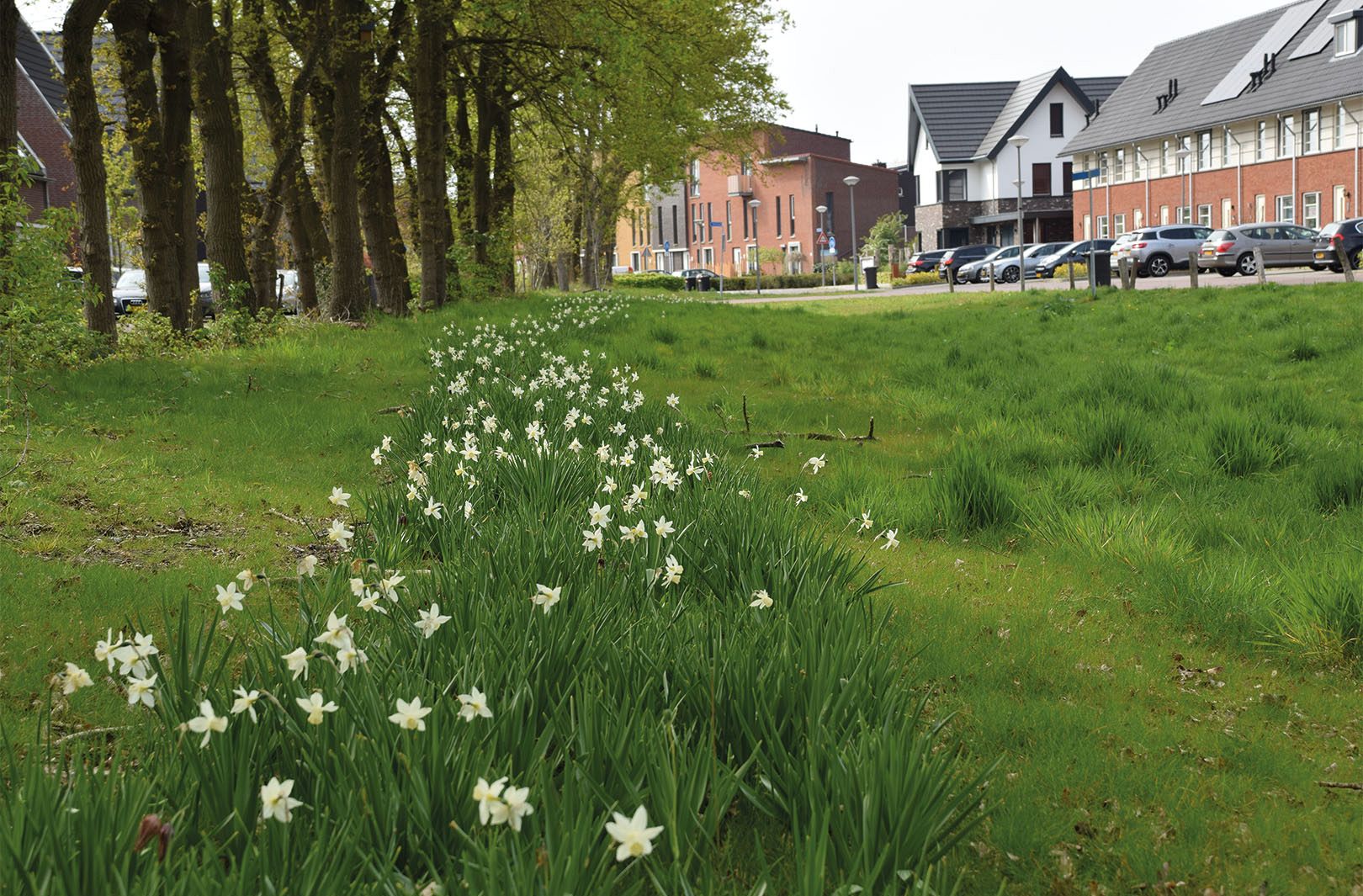

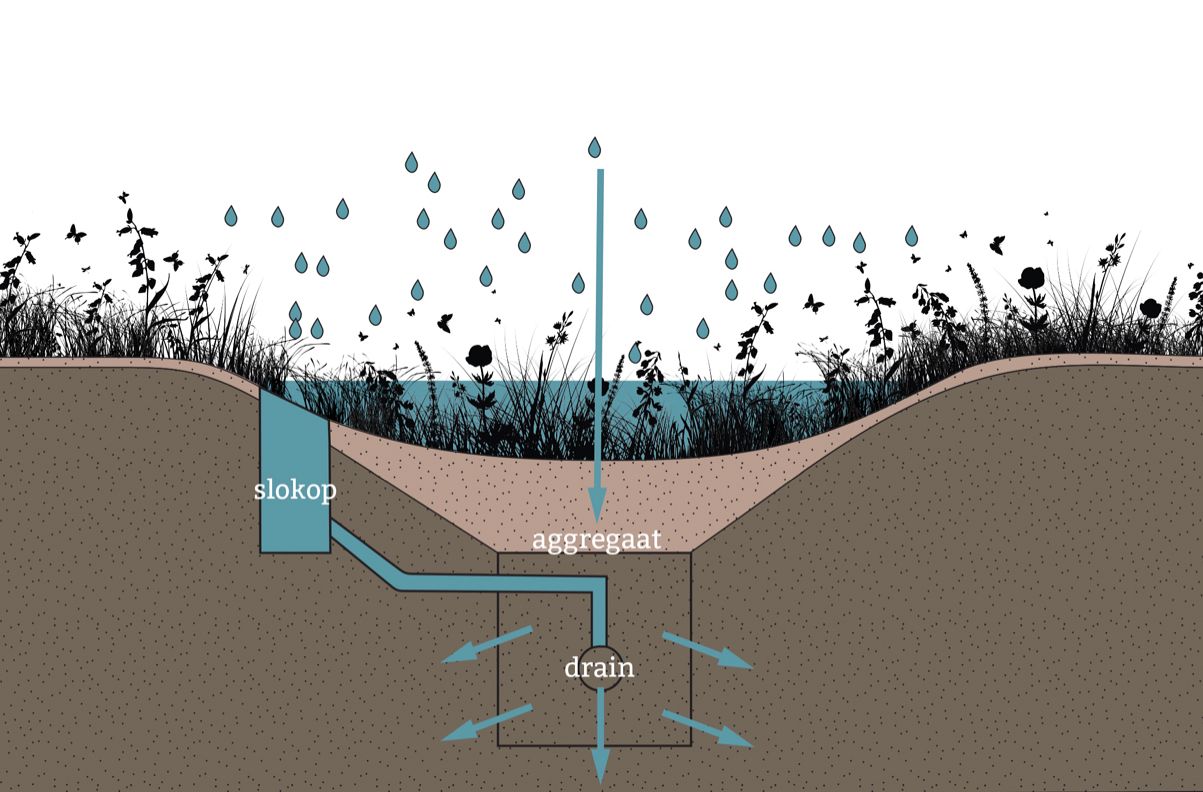
Wet Bioswale
The illustration next to this text shows a bioswale in its wet state, when it is submerged under water. Rainwater is filtered through the top layer of the bioswale and gradually seeps back into the ground, improving water quality. This natural filtration process is essential for maintaining a healthy ecosystem. If too much water accumulates in the bioswale, the excess water is stored through the overflow outlet and drained away.
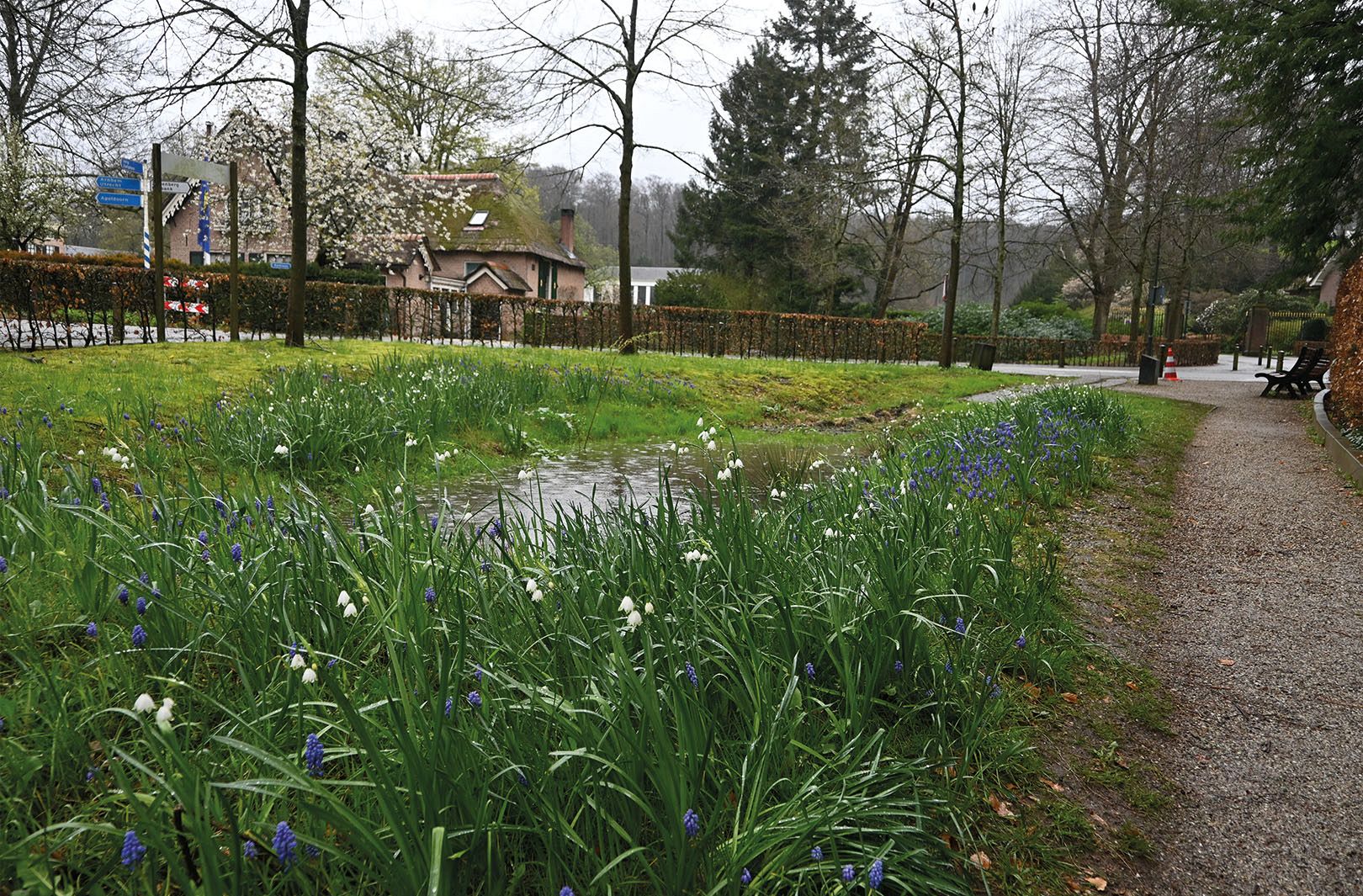
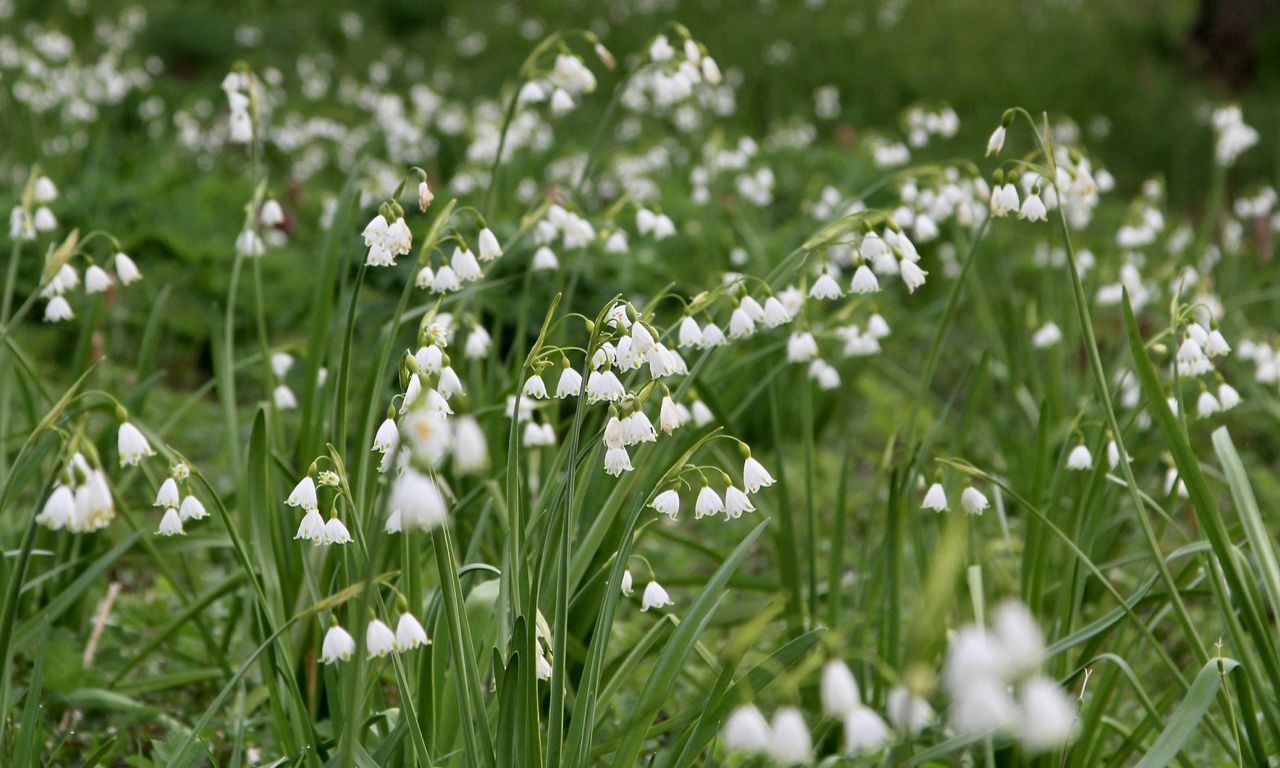


(NATURAL) BIOSWALE PLANTING
A naturally planted bioswale is not only an aesthetic enhancement but also offers numerous benefits. Its infiltration capacity increases, as not only does the percolation layer function effectively, but the plants also store water in their hollow stems. Additionally, a nature-friendly bioswale requires less maintenance than a grass-covered bioswale, which needs to be mowed more frequently.
The tall, flowering plants in a natural bioswale also contribute to urban biodiversity, providing habitats for many insects, birds, and mammals, such as hedgehogs. Furthermore, diverse planting promotes a well-rooted, aerated soil with a healthy soil ecosystem, ensuring that the ground remains permeable over the long term.
SUITABLE PLANT SELECTION
Plants that are suitable for a bioswale are not always marsh plants, but they must be able to withstand dynamic and changing conditions: they should endure both dry periods and (very) wet situations. Grass is not suitable for bioswales, as lawn grasses do not tolerate oxygen deficiency well. A (perennial) herbaceous vegetation, with or without the combination of trees, is ideal.
Additionally, a limited selection of flower bulbs can be applied in a bioswale. Flower bulbs can withstand drought during their dormant period, and some species thrive exceptionally well in wet to moist locations. In all cases, however, it is essential that drainage is optimal. Furthermore, a reasonable level of soil fertility is necessary for healthy growth. To ensure optimal naturalization, the mowing management must be adjusted to allow the foliage to die back properly, so that the bulb can store enough nutrients for the next growing season.
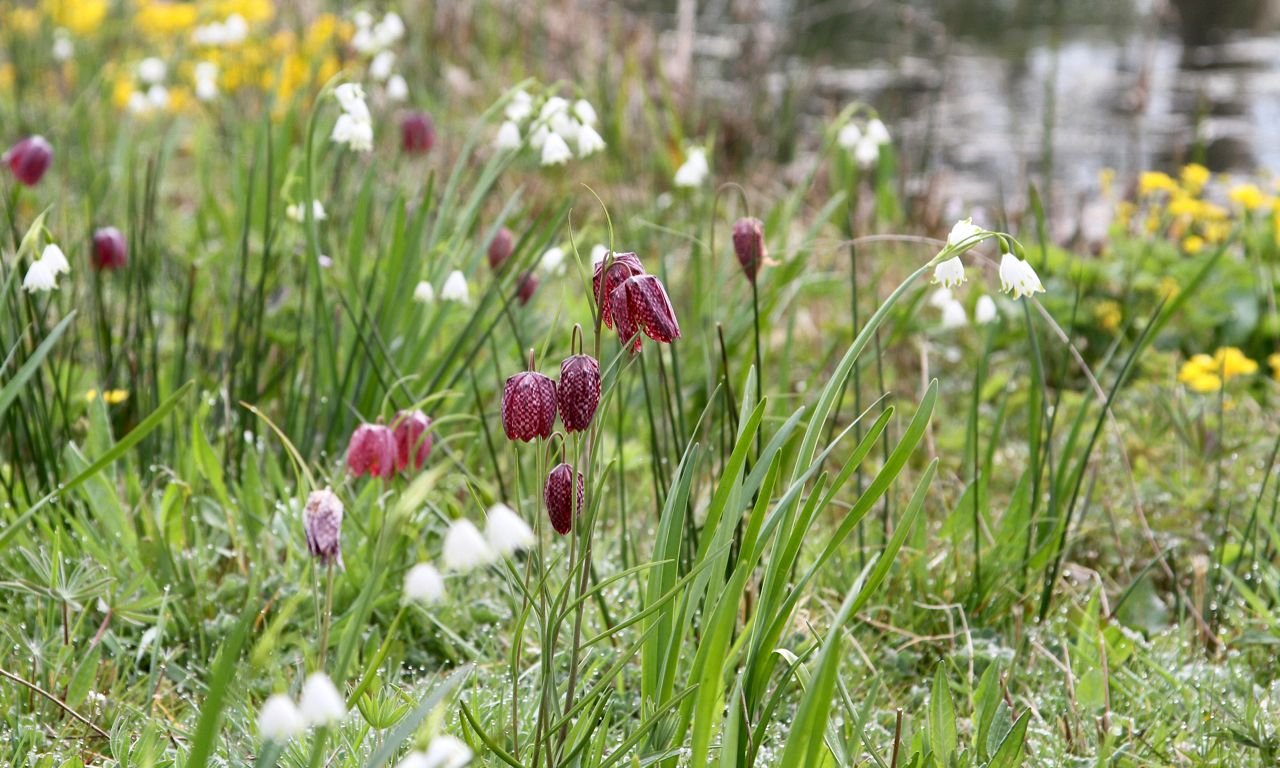

SUITABLE FLOWER BULBS
For successful planting in bioswales, certain flower bulbs are particularly well-suited. These species are not only attractive but also capable of thriving in the varying conditions of a bioswale, where they can endure both dry and wet periods. Below is a list of recommended flower bulbs that contribute to the biodiversity and visual appeal of your bioswale:






















